The tomato genome has been published in Nature on May 31, 2012, culminating years of work by the Tomato Genome Consortium, a multi-national team of scientists from 14 countries. The Tomato Genome Consortium started its work in 2003, when scientists analyzed the DNA sequence of tomato using the most modern equipment available at the time. Consortium researchers report that tomatoes possess some 35,000 genes arranged on 12 chromosomes and chromosome 0 (all scaffolds that could not be placed on either of the 12 tomato chromosomes by either the genetic or physical maps were placed on an artificial "chromosome 0". The scaffolds on this chromosome are ordered from large to small and unoriented.). Fortunately, with the recent introduction of so-called "next generation sequencing" technologies, the speed of data output increased 500-fold and enabled the project to move on efficiently to its conclusion. Copy of data used in database development and analysis work is available (Downloaded from: ftp://ftp.solgenomics.net/tomato_genome/wgs/assembly/build_2.40/)
All the 12 chromosomes were chopped into manageable range of 50000 bp using
PERL script. These fragments were given to MIcroSAtellite identification
tool (MISA) to identify and find the location of perfect and compound
microsatellites for all the chromosomes of tomato genome. The SSR
numbers, motifs, repeat number, length of the repeat, size of the repeat,
repeat type, GC content, start and end position of the repeat and SSR
sequence has been compiled. Chromosome wise description of the SSRs have
been tabulated as well as represented as graphs. The mono, di, tri, tetra,
penta and hexa type of microsatellites have been plotted to show the
abundance of the type in chromosomes.In addition, facility to locate the
SSRs on chromosomes based on the position number is incorporated which may
be very useful to the biotechnologists. The tabulation of simple
versus compound shows the proportion of the same.
Scientific name |
Common name |
Chr. no. |
Genome Size |
Estimated No. of Genes |
Solanum lycopersicum |
|
12 |
~950 MegaBases |
35,000 genes |
Table 1. Description of Tomato genome
Type |
Number |
Percentage |
Simple |
127207 |
86.77 |
Compound |
19395 |
13.23 |
Total |
|
100.00 |
Table 2. Description of Microsatellite types in Tomato genome
Motif Type |
Number |
Percentage
(%) |
Mono |
73556 |
57.82 |
Di |
39125 |
30.76 |
Tri |
12576 |
9.89 |
Tetra |
1565 |
1.23 |
Penta |
232 |
0.18 |
Hexa |
153 |
0.12 |
Table 3. Motif wise distribution of Microsatellites in Tomato genome
Chromosome |
Simple |
Compound |
Mono |
Di |
Tri |
Tetra |
Penta |
Hexa |
1 |
8995 |
4632 |
1476 |
194 |
35 |
19 |
2311 |
2 |
6401 |
2746 |
867 |
95 |
15 |
6 |
1363 |
3 |
6637 |
3370 |
1107 |
150 |
18 |
21 |
1572 |
4 |
6332 |
3268 |
1076 |
115 |
24 |
13 |
1499 |
5 |
5714 |
3300 |
1028 |
128 |
17 |
11 |
1632 |
6 |
5105 |
2652 |
861 |
102 |
8 |
9 |
1219 |
7 |
5801 |
3097 |
1045 |
137 |
22 |
11 |
1580 |
8 |
5974 |
3052 |
966 |
136 |
19 |
11 |
1556 |
9 |
5886 |
3275 |
1098 |
118 |
20 |
17 |
1613 |
10 |
5369 |
3041 |
910 |
140 |
15 |
12 |
1417 |
11 |
5005 |
2640 |
916 |
91 |
16 |
3 |
1360 |
12 |
5365 |
3034 |
995 |
126 |
20 |
18 |
1687 |
0 |
972 |
1018 |
231 |
33 |
3 |
2 |
586 |
Table 4. Motif wise distribution of Microsatellites in Tomato chromosomes
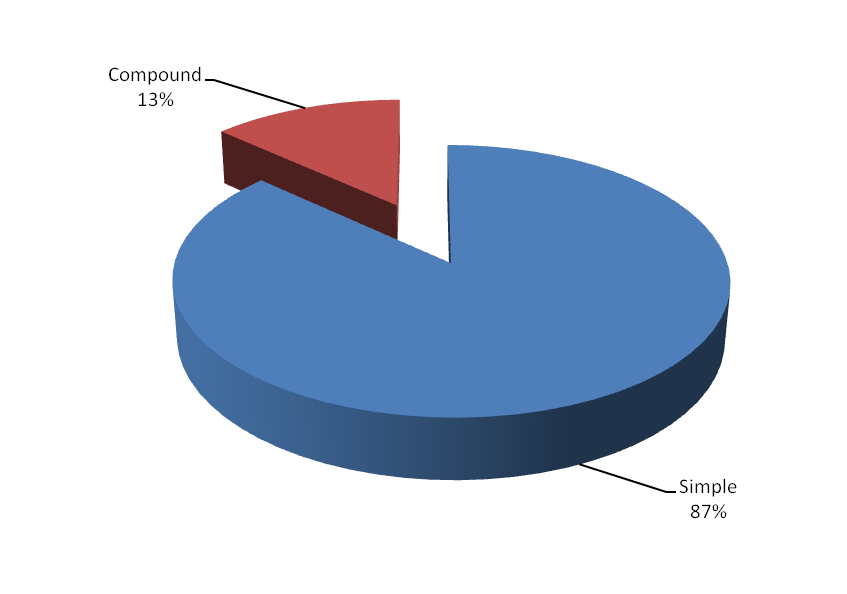
Figure 1. Distribution of SSR marker type
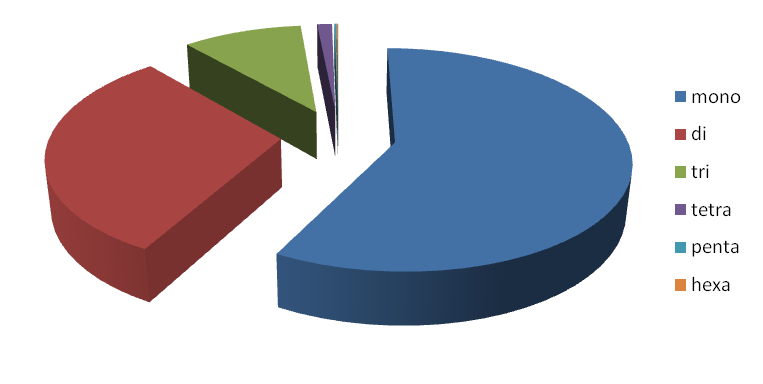
Figure 2. Distribution of repeat types
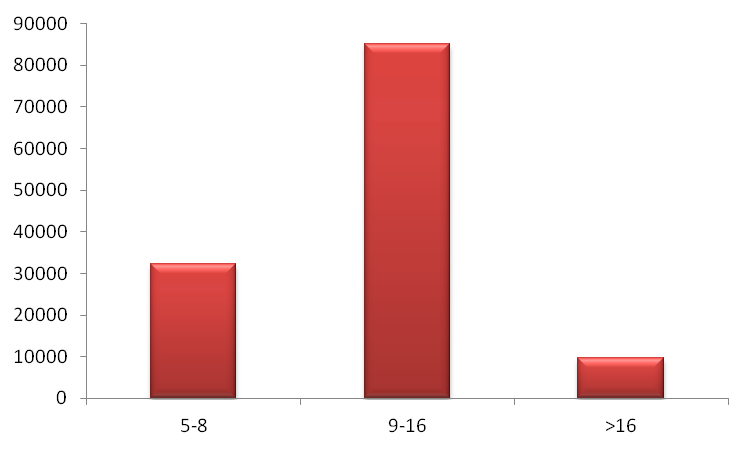
Figure 3. Distribution of repeat kinds
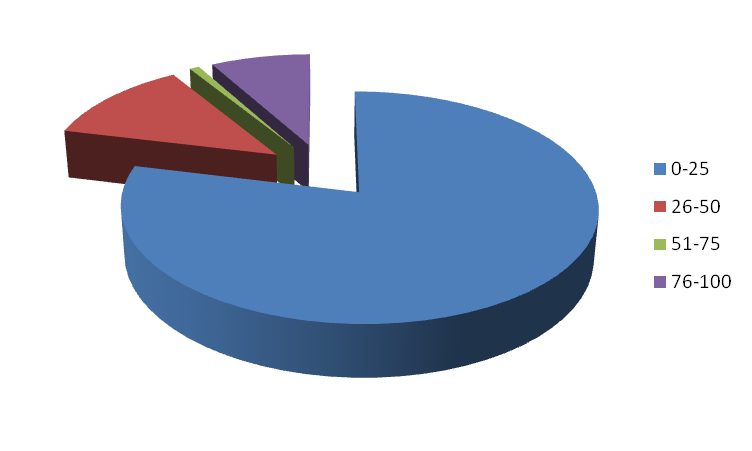
Figure 4. Distribution based on GC Content
|
